The superior colliculus is one of the front pair of round eminences of the midbrain that add to visual capacity, including the age of eye developments. In non-mammalian vertebrates, this structure is alluded to as the optic tectum.
In warm-blooded animals, the superior colliculus structures a significant part of the midbrain. It is a matched structure and, along with the combined substandard colliculi structures.
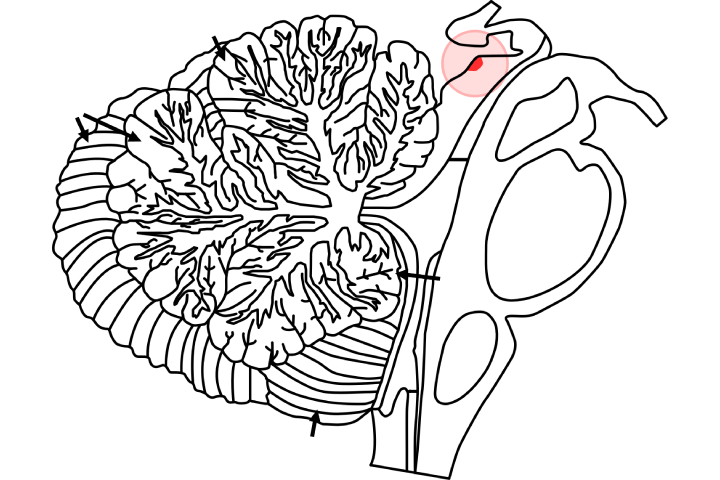
The unrivalled colliculus is a layered structure with various layers that differ by species. The layers can be gathered into the shallow layers (layer optical or more) and the more profound residual layers. Neurons in the superficial layers get an immediate contribution from the retina and react solely to visual improvements.
Numerous neurons in the more profound layers likewise respond to different modalities, and some react to upgrades in various modalities. The more profound layers additionally contain a populace of engine-related neurons, fit for actuating eye developments just as different reactions.
source: Wikipedia
Table of Contents
1. Where Are the Superior Colliculi Found?
Midbrain
There are two superior colliculi in the midbrain. They are evenly situated, one on either side of the brainstem; they structure two knocks on the back outside surface of the brainstem. The superior colliculi are only underneath the thalamus or more than the two mediocre colliculi.
2. Is the Superior Colliculus Part of the Thalamus?
The superior colliculus is a layered synaptic structure. The two superior colliculi sit beneath the thalamus and encompass the pineal organ in the mammalian midbrain. It involves the dorsal part of the midbrain, back to the periaqueductal dark, and promptly better than the mediocre colliculus.
3. What Occurs if the Superior Colliculus is Harmed?
Sore of the LEFT better colliculus brings about failure than turn head reflexively to the Right (Contra.) upon visual (or somatosensory and hear-able) improvements on the Right. Other Note: Superior colliculus is likewise engaged with the control of eye developments.
4. What is the primary capacity of the superior colliculus?
Visual System
The superior colliculus in all well-evolved creatures comprises seven layers, six of which are marked. The retina’s projection ends in the three shallow layers – the layer zone, layer Griseum superficial, and the layer optimum.
The moderately little ipsilateral arm to the predominant colliculus ends in patches’ progression in the superior colliculus’ rostromedial bit.
The retinotopic association of the unrivalled colliculus is steady among warm-blooded animals: the zero vertical meridians are spoken to rostrally, and the most fringe some portion of the contralateral visual field is spoken to caudally.
The upper visual field is spoken to medially in the superior colliculus, and the lower visual field is spoken to along the side. As noted over, the ipsilateral hemifield’s portrayal is confined to the most rostral zone of the superior colliculus.
The retinal image is the equivalent in all retina beneficiary layers. The predominant colliculus gets generous contribution from the ipsilateral essential visual cortex. In the more profound layers of the superior colliculus, numerous cells react to somatosensory and hear-able upgrades just as visual information.
The primary somatosensory contribution to the superior colliculus is from the bristles.
Blood Supply and Lymphatics
The unrivalled colliculus gets its blood gracefully from both the collicular conduit and the posteromedial choroidal corridor. These are both proximal branches from the cerebral back hall.
It is essential that the superior cerebellar corridor, which branches from the basilar vein, is here and credited to gracefully the predominant colliculus.
Lymphatics of the mind were as of late found, with one examination recognizing the presence of cerebrum lymphatic endothelial cells over the optic tectum of zebrafish, specifically take-up explicit macromolecules.
Surgical Considerations
The superior colliculus’ medical procedure ought to be drawn closer with alert as the midbrain is a persuasive region related to huge dangers from Surgical resection.
The medical system is for tectal gliomas. Nonetheless, entanglements incorporate visual deformities, Parinaud condition, mutism, and decreased vegetative state followed by death. Hence, Surgical resection is regularly saved, dependent on the movement of the tumour.
Treatment for tectal gliomas is as yet disputable and easy to refute. Yet, with the coming of novel neurosurgical microsurgical procedures, this once unavailable zone is presently congenial with expanded wellbeing.
Clinical Significance
Direct harm to the superior colliculus has been tried in rhesus monkeys just as rodents and has brought about clinical indications. Specialists found that the monkeys damage the better colliculus than have visual shortfalls only as hindrances in look shifts.
Rodents with collicular harm showed an absence of arranging reflex and interruption when given visual or hear-able improvements when contrasted and ordinary or rodents with visual cortex sores. In people, harm to the association with the prefrontal cortex has demonstrated to be related to impacts to consider.
Sores Hindering
Sores hindering inhibitory contributions from the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex to the unrivalled colliculus caused expanded distractibility in one patient.
Tectal glioma, an uncommon low-quality tumour, is a state of specific concern. It influences the unrivalled and substandard colliculi just as the cerebral water system, bringing about expanded intracranial weight and long haul morbidities.
It essentially controls a pediatric populace with indications, including constant cerebral pains, visual shortfalls, and neurological hindrance. Therapy generally includes shunting the cerebrospinal liquid, radiation treatment, chemotherapy, or reasonable medical procedures if the tumour keeps amplifying.
5. The Direct Effects of Light on Sleep
Light and dim effects affect rest and attentiveness in well-evolving creatures, yet the neural systems essential these impacts are inadequately perceived.

Injuries of the visual cortex or the superior colliculus–pretectal region were acted in pale-skinned person rodents to decide retinorecipient territories that intercede the impacts of light on conduct, including quick eye development rest setting off by lights-off and redistribution of non-fast eye development snooze harsh light–dull cycles.
Alarming Impacts
Direct light has immediate alarming impacts in diurnal warm-blooded creatures; for example, people though dimness advances rest; nighttime creatures show the contrary results, with splendid light actuating rest and murkiness expanding alertness.
Intense reactions to changes in lighting conditions vary from circadian entrainment by light in that they happen promptly because of the lighting change and don’t continue without incitement.
Such reactions now and again are alluded to veiling in the circadian writing, implying that the light upgrade might be following up on rest, and alertness focuses straightforwardly without nearly prompting changes in the circadian pacemaker.